The international English standardized exams have gained notorious importance in Peru, as well as the other countries in Latin America, and all over the world. What is the real reason for this? None other than the need to have a valid method of appraising the extent at which learners are able to understand and speak the language of Chaucer and Whitman.
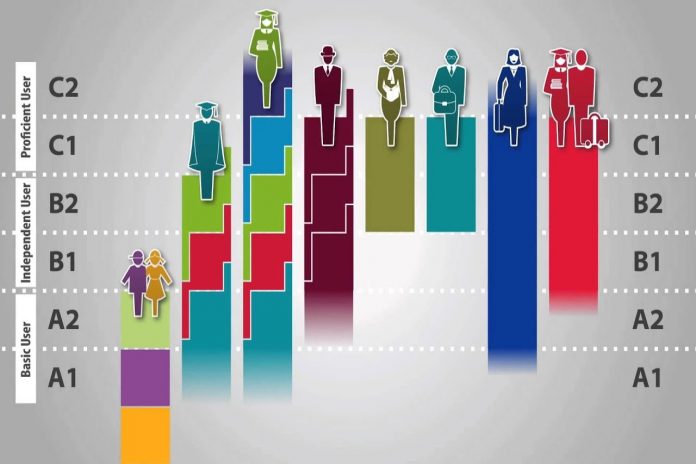
First of all, a fairly accurate unit of measurement was required. The old classification of beginner, intermediate and advance wasn’t holding the water. There were no precise boundaries between these, and other intermediate subcategories like pre-intermediate and upper-intermediate, for example. Each educational institution would set its own requirements for upgrading to the next subcategory or category and establish their own labels as to what an individual in each of the brackets should know. The ensuing problem sprang, not surprisingly, when a student went from a school to another and their knowledge did not reach their expectations for the tag they bore or surpassed them widely. There was no way to know how much a student knew short of sitting them to an English exam.
BABEL’S EUROPE
Multilingualism is common for the countries of Europe, particularly in nations such as Switzerland, the Netherlands or Belgium. So it is no surprise that the Swiss Federal Authorities, in the Swiss municipality of Rüschlikon, were pioneers in organizing an intergovernmental symposium to look for the objectives, evaluation and certification of language learning in Europe. This meeting, held in 1991, found the need to develop a common European framework for languages to improve the recognition of language qualifications and help teachers to operate under the same basic parameters. A project to develop language-level classifications for certification to be recognized across Europe ensued.
They were certainly not alone. The Council of Europe had been working since 1989, and continued until 1996, in their project “Language Learning for European Citizenship” with the purpose of providing a method of learning, teaching and assessing that could be applied to all the languages in Europe. Continued deliberation and labor eventually led to the development of the Common European Framework of Reference for Language Learning, Teaching and Assessment which is the result of the collaboration of many members of the teaching profession across Europe and other places. It was in 2001 that the European Union Council recommended using the CEFR to set up systems of validation of language ability, an initiative that it is becoming widely accepted as the European standard for rating an individual’s language proficiency. The system endeavours to put forward a clear, coherent and complete basis for the elaboration of language syllabuses and curriculum guidelines, the drawing of teaching materials, and the evaluation of language aptitude.
The English University of Cambridge established UCLES (University of Cambridge Local Examinations Board) as early as 1858 (a similar organization had been set up by the University of Oxford one year before) to set school leaving examinations for non-members of the university and began the first overseas examinations in 1864. They started to develop different tests for diverse levels of speakers. By 1955 they were conducting over 100,000 examinations.
With the advent of the 21st century and the establishment of the CEFR, the British exams turned to reflect English speaking abilities expressed in their six categories. There are no passing or failing grades, just a description of what the exam takers are capable of doing.
Across the Atlantic there is another huge organization dedicated to administer a variety of English proficiency exams. It’s the Educational Testing Service that claims to score more than 50 million tests annually in over 180 countries. They’ve been delivering tests since 1947. Among them are TOEFL, TOEIC, GRE, SAT. The popular and well known TOEFL was designed to establish whether the candidate is able to conduct undergraduate or graduate universities studies in English. It went from a hand written version to a computerized one and now an internet based variety. Although it wasn’t put together around the CEFR, its results can be measured in terms of it.
REFERENCES
Cambridge Assessment, Our Heritage. http://www.cambridgeassessment.org.uk/about- us/who-we-are/our-heritage/ Retrieved June 20, 2017.
Educational Testing Service History. http://www.fundinguniverse.com/company-histories/educational-testing-service-history/ Retrieved June 20, 2017.
International English Language Testing System. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_English_Language_Testing_System#frb-inline. Retrieved June 20, 2017.
Estimated reading time: 3 minutes, 34 seconds











What a great overview of both systems.
Comments are closed.